MOTIVATION AND EMOTION
What is Motivation?
- A need or desire that energizes and directs behavior
What is Instinct Theory?
- We are motivated by out inborn automated behaviors.
What does Drive Reduction Theory mean?
- The idea that a physiological need creates an aroused tensions state (a drive) that motivated an organism to satisfy the need.
- The need is usually to maintain homeostasis
- We are not only pushed by our needs but pulled by our incentives.
- A positive or Negative environmental stimulus that motivates behavior
- "Different levels of arousal depending on activity
What does Maslow's Hierarchy or Needs mean?
- We are motivated by needs, and all needs aren't created equal.
- We are driven to satisfy the lower level need first.
An example of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
- Food, and Water
What does Hunger mean?
- Both Physiological and Psychological
What is the Physiology of Hunger?
- Washburn's study showed hunger was partially related to the stomach.
Biological Basis of Hunger
- Hunger does not come from the stomach
- Hunger comes from our brain
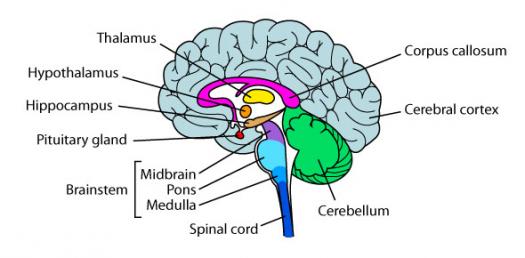
Which part of the brain controls hunger?
- The Hypothalamus
Types of Hypothalamus
- Lateral
- When stimulated it makes you hungry
- Ventromedial
- When Stimulated you feel full
Set Point Theory
- Specific body weight maintained
- The Hypothalamus acts like a thermostat
- Wants to maintain a stable weight
- Activate the lateral when you diet and activated the Ventromedial when you start to gain weight.
How does the Hypothalamus work?
- Leptin: A protein produced by bloated fat cells
Body Chemistry
- Glucose and Insulin (Hormone Insulin converts glucose to fat, regulate hunger levels)
Psychological Aspects of Hunger
- Internal Vs. External
Eating Disorders
- Bulimia Nervosa
- Characterized by binging (eating large amounts of food) and purging (getting rid of the food)
- Anorexia Nervosa
- Starve themselves to below 85% of their normal body weight
- Sees themselves as fat
- Vast majority are women
- Obesity
- Severely overweight to the point where it causes health issues
- Incentive Homeostasis
- Environmental stimulus
- Constant/ Balance
What does Achievement Motivation mean?
- What motivates us to do work?
- (School, jobs, sports, video games)
What is Intrinsic Motivators?
- A reward we get internally, such as enjoyment of satisfaction
What is Extrinsic Motivators
- A reward that we get for accomplishments from outside ourselves (grades or money or etc...)
- Works great in the short run
What is Management Theory
Theory X
- (Managers believe that employees will work only if rewarded with benefits or threatened with punishment.
- Think employees are extrinsically motivated
- Only interested in Maslow's lower needs
Theory Y
- Managers believe that employees are internally motivated to do good work and policies should encourage this internal motive.
- Interested in Maslow's higher needs.
Theory of Emotion
What is the James Lange Theory?
- Experience of emotion is awareness of psychological repsonses to emotion- arousing stimuli
What is a stimulus
- Spotting the danger/ surrounding- "Sight an oncoming car*
- Reaction- Pounding heart
- Emotion- Fear
What is emotion?
- We feel emotion because of biological changes caused by stress.
- The body changes, our mind recognizes the feeling.
What is the Cannon- Bard Theory of Emotion?
- Emotion- arousing stimuli simultaneously trigger:
- Physiological responses
- Subjective experience of emotion.
- Fear + Emotion [sight of car]
Experience Emotion
- Adaptation- Level Phenomenon
- Tendency to form judgments relative to a "neutral" level: "brightness of lights", "Volume"
What is Relative Deprivation?
- Perception that one is worse off relative to those with whom one compares oneself.
Good blog, but I suggest you could improve it by adding pictures and videos about the topic talked about. I also noticed that you could add some other information such as what a polygraph measures (changes in the heart rate and blood pressure), etc.
ReplyDeleteThank you! I'll go back and add those things
DeleteI think that adding an example of relative deprivation would be useful
ReplyDeleteAlright thank you for your tip
Delete