BIOLOGICAL BASIS OF BEHAVIOR
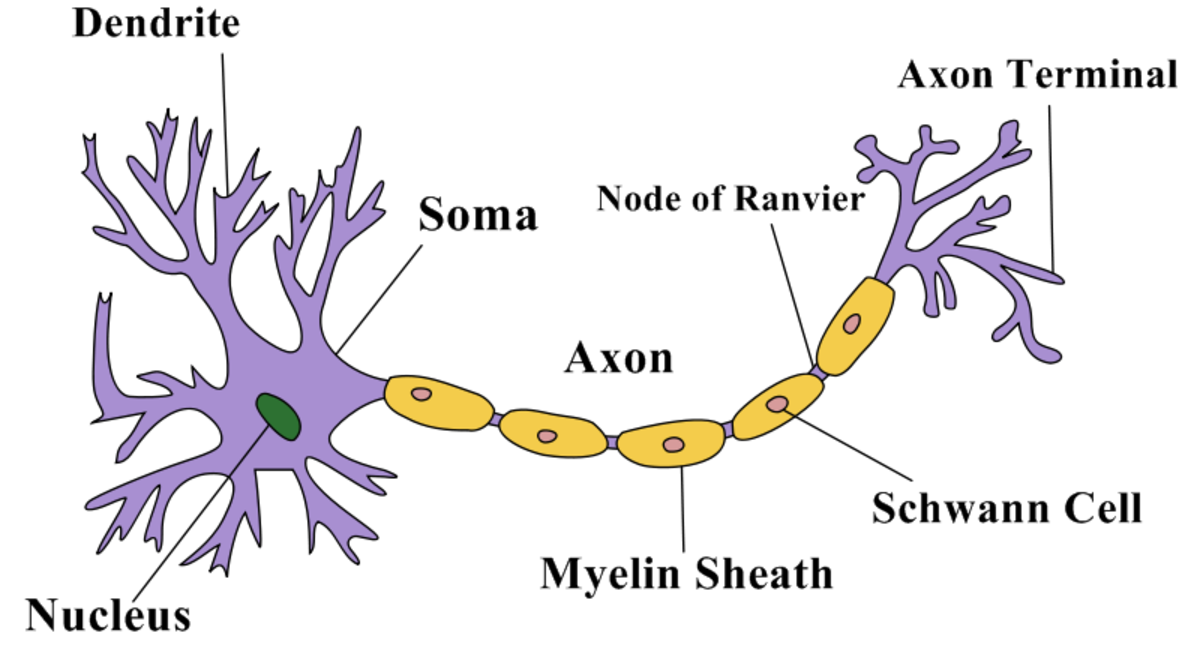
Neuron Structure
- Nucleus contained inside
- Cell life support center
Dendrites
- Receives messages from other cells
- Finger like
Axon
- Passes messages away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
- Covers the Axon of Neurons
- Helps with Neutral impulses and speed.
Neural Impulses
- Electrical signal travelling down the axon
Terminal Branches of Axon
- Form junctions with other cells.
What is the Synapse?
- The space in between the cell
How does a Neuron Fire?
- It is an electrochemical process
- Electrical inside the neuron
- Chemical outside the neuron (in the synapse in the form of a neurotransmitter)
What is Action Potential?
- Action Potential is what the "firing" is called
All or None Response
- The idea that either the neurons fire or does not- No halfway firing
- Like a gun- "You either fire or you don't"
What is a Neurotransmitter?
- Chemical messages released by terminal buttons through the Synapse.
How do we study the brain?
- Accident
- Lesions (Remove or destroy parts of the brain)
TOOLS USED
EEG
- Electroencephalogram
- Used mainly in sleep research
CAT SCAN
- Computerized Axial Tomography
- 3-D X-ray of the brain
- Good for tumor locating but tells us nothing about the function.
MRI
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Takes still pictures
PET SCAN
- Positron Emission Tomography
- Measures how much of a chemical the brain is using. (Usually glucose consumption)
- Combination of the PET scan and MRI
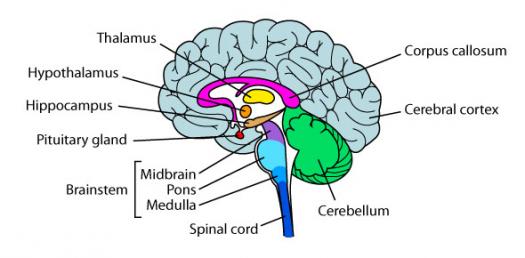
What is the Corpus Callosum?
- Connects the two hemispheres of the Cerebral Cortex
What happens when the Corpus Callosum is removed?
- Split brain patient
Define Brain Plasticity
- The ability of our brain to form new connections after neurons damage.
Types of Neurotransmitters
Acetylcholine (ACH)
- Deals with motor movement and memory
- Lack of ACH had been linked to Alzheimer's
Dopamine
- Deals wit motor movement and alertness
- Lack of Dopamine has been linked to Parkinson's Disease
- Too much has been linked to Schizophrenia.
- Involved with mood control
- Lack of Serotonin has been linked to clinical depression
What is Endorphins?
- Involved in pain control
- Many of our most addictive drugs deal with Endorphins
What is GABA?
- The brains major inhibitory neurotransmitter
- Causes Schizophrenia and Insomnia
What is Glutamate?
- Glutamate creates links between neurons that form the basis of learning and long term memory.
- If taken in excess it can cause over stimulation of the brain resulting in a Seizure
- Avoid foods with MSG
What are Norepinephrine's?
- It is a fight or Flight
- Controls alertness and arousal
- Elevates the heart rate, circulation and respiration
- Probably can put you in a depressed mood.
Drugs can be...
- Agonist (Makes neurons fire)
- Antagonist (Stops Neurons from firing)
- Reuptake Inhibitors (Block Neurotransmitters from transmitting)
No comments:
Post a Comment