MOTIVATION AND EMOTION
What is Motivation?
- A need or desire that energizes and directs behavior
What is Instinct Theory?
- We are motivated by out inborn automated behaviors.
What does Drive Reduction Theory mean?
- The idea that a physiological need creates an aroused tensions state (a drive) that motivated an organism to satisfy the need.
- The need is usually to maintain homeostasis
- We are not only pushed by our needs but pulled by our incentives.
- A positive or Negative environmental stimulus that motivates behavior
- "Different levels of arousal depending on activity
What does Maslow's Hierarchy or Needs mean?
- We are motivated by needs, and all needs aren't created equal.
- We are driven to satisfy the lower level need first.
An example of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
- Food, and Water
What does Hunger mean?
- Both Physiological and Psychological
What is the Physiology of Hunger?
- Washburn's study showed hunger was partially related to the stomach.
Biological Basis of Hunger
- Hunger does not come from the stomach
- Hunger comes from our brain
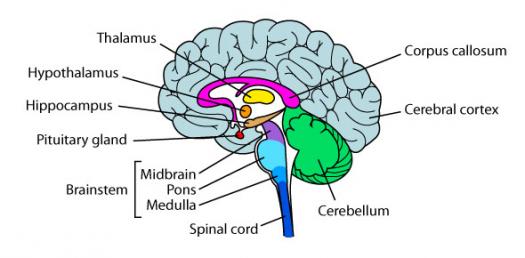
Which part of the brain controls hunger?
- The Hypothalamus
Types of Hypothalamus
- Lateral
- When stimulated it makes you hungry
- Ventromedial
- When Stimulated you feel full
Set Point Theory
- Specific body weight maintained
- The Hypothalamus acts like a thermostat
- Wants to maintain a stable weight
- Activate the lateral when you diet and activated the Ventromedial when you start to gain weight.
How does the Hypothalamus work?
- Leptin: A protein produced by bloated fat cells
Body Chemistry
- Glucose and Insulin (Hormone Insulin converts glucose to fat, regulate hunger levels)
Psychological Aspects of Hunger
- Internal Vs. External
Eating Disorders
- Bulimia Nervosa
- Characterized by binging (eating large amounts of food) and purging (getting rid of the food)
- Anorexia Nervosa
- Starve themselves to below 85% of their normal body weight
- Sees themselves as fat
- Vast majority are women
- Obesity
- Severely overweight to the point where it causes health issues
- Incentive Homeostasis
- Environmental stimulus
- Constant/ Balance
What does Achievement Motivation mean?
- What motivates us to do work?
- (School, jobs, sports, video games)
What is Intrinsic Motivators?
- A reward we get internally, such as enjoyment of satisfaction
What is Extrinsic Motivators
- A reward that we get for accomplishments from outside ourselves (grades or money or etc...)
- Works great in the short run
What is Management Theory
Theory X
- (Managers believe that employees will work only if rewarded with benefits or threatened with punishment.
- Think employees are extrinsically motivated
- Only interested in Maslow's lower needs
Theory Y
- Managers believe that employees are internally motivated to do good work and policies should encourage this internal motive.
- Interested in Maslow's higher needs.
Theory of Emotion
What is the James Lange Theory?
- Experience of emotion is awareness of psychological repsonses to emotion- arousing stimuli
What is a stimulus
- Spotting the danger/ surrounding- "Sight an oncoming car*
- Reaction- Pounding heart
- Emotion- Fear
What is emotion?
- We feel emotion because of biological changes caused by stress.
- The body changes, our mind recognizes the feeling.
What is the Cannon- Bard Theory of Emotion?
- Emotion- arousing stimuli simultaneously trigger:
- Physiological responses
- Subjective experience of emotion.
- Fear + Emotion [sight of car]
Experience Emotion
- Adaptation- Level Phenomenon
- Tendency to form judgments relative to a "neutral" level: "brightness of lights", "Volume"
What is Relative Deprivation?
- Perception that one is worse off relative to those with whom one compares oneself.