SENSORY NEURONS/ MOTOR NEURONS/ INTERNEURONS
SENSORY OR AFFERENT NEURONS
- Taking information from the senses to the brain.
EXAMPLE
- How quick do you react?
INTERNEURONS
- Takes messages from the sensory Neurons to the other parts of the brain or to the motor Neuron.
EXAMPLE
- A gossip
MOTOR NEURONS
- Takes information from the brain to the rest of the body.
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
What two parts make up the nervous system?
- The peripheral and the Central
- The Spinal Cord
- Brain and Spinal Cord
- Automatic and Somatic
- Controls self regulated action of internal organs and glands.
- Controls voluntary movements of the skeletal muscle.
- Flight or Fight response
- Adrenal Gland
- Pupil dilate, Inhibits digestions, Stimulates Norepinephrine
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
What does the Endocrine System mean?- A system of glands that secrete hormones.
- Similar to the Nervous system, except hormones work a lot slower than neurotransmitters
- Hormones are slow
- Neurotransmitters are fast
PARTS OF THE BRAIN
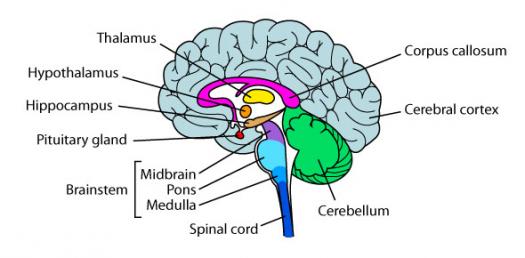
HINDE BRAIN
- The structure on tip of our spinal cord
- Controls our basic biological structures
PARTS OF THE HINDBRAIN
Medulla
- Located above the spinal cord
- It controls your heartbeat, blood pressure, and breathing
Pons
- Alarm Clock
- Located above the Medulla
- Connects the Hindbrain with the Midbrain and the Forebrain
- Involved in Facial Expression
Cerebellum
- Located at the bottom rear of the brain
- Known as the little brain
- Influences memory and learning
- Coordinated voluntary muscle movement and balance
PARTS OF THE MIDBRAIN
What is the function of the Midbrain?
- To coordinate simple movements with sensory information
Important structure….
- Reticular Formation/ Activation (Controls arousal and our ability to focus)
Function
- What makes us human
- The largest part of the brain
- Made up of the Thalamus, Cerebral Cortex, and the Limbic System
PARTS OF FOREBRAIN
- Thalamus
- Switch brain of the brain
- Does many different things at the same time (Multitasking)
- Relays sensory information except the sense of smell
- Receives Sensory signals from the Spinal Cord and sends them to other parts of the Forebrain.
LIMBIC SYSTEM
- Hypothalamus
- Most important structure in your brain
- Controls and regulates body temperature, hunger, thirst, sexual behavior, and the Endocrine System.
- Hippocampus
- Involves processing, and storing of memories
- Learn information and retain it
- Amygdala
- Deals with anger, fear and arousal [EMOTION]
- Pituitary Gland
- Promotes Growth
What is the Cerebral Cortex?
- Made up of Densely packed neurons that we call (gray matter)
- Control and Processing center
What are Wrinkles in relation to the brain?
- Fisher, folds in the brain
The Brain
- The brain is divided into two hemispheres
- LEFT HEMISPHERE
- Logical and Sequential tasks
- RIGHT HEMISPHERE
- Special and creative tasks
LOBES
Frontal Lobe
- Located behind the forehead (Speaking, muscle movements, making plans and judgements)
- Sends signals to our bodies coordinating muscle movements
- Broca's Areas
- Responsible for controlling muscles that produce speech
- Broca's Aphasia
- Located at the top and rear of the Cerebral Cortex
- Sensory Cortex
- Contains the Parietal Lobe
- Receives incoming touch sensations from the rest of the body
- Most of the Parietal Lobes are made up of association areas.
What is an Association Area? (Highly Functioning)
- Any area that is not associated with receiving sensory information or coordinating muscle movement.
- Deals with vision
- Contains the Visual Cortex
- Located in the back of the head
- Visual Cortex
- Interprets messages from the eyes into images we can understand
- Processes sound that is sensed by the ear
- Located just above the ears
What is Auditory Cortex?
- Used for hearing and processing sound (Function)
Wernicke's Area
- Processes sound and interprets written and spoken speech
Wernicke's Aphasia
- Unable to understand language.
- The syntax and grammar is jumbled.
